 Zobacz na TensorFlow.org Zobacz na TensorFlow.org |  Uruchom w Google Colab Uruchom w Google Colab |  Zobacz na GitHub Zobacz na GitHub |  Pobierz notatnik Pobierz notatnik |  Zobacz modele piasty TF Zobacz modele piasty TF |
Wstęp
Modele klasyfikacji obrazów mają miliony parametrów. Szkolenie ich od zera wymaga wielu oznaczonych danych treningowych i dużej mocy obliczeniowej. Transfer uczenia się to technika, która znacznie skraca ten proces, biorąc fragment modelu, który został już przeszkolony w odniesieniu do powiązanego zadania, i ponownie wykorzystując go w nowym modelu.
Ten Colab pokazuje, jak zbudować model Keras do klasyfikowania pięciu gatunków kwiatów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu TF2 SavedModel z TensorFlow Hub do ekstrakcji cech obrazu, przeszkolonego na znacznie większym i bardziej ogólnym zbiorze danych ImageNet. Opcjonalnie ekstraktor cech można wytrenować („dostroić”) wraz z nowo dodanym klasyfikatorem.
Szukasz narzędzia?
To jest samouczek kodowania TensorFlow. Jeśli chcesz narzędzie, które właśnie buduje model TensorFlow lub TFLite dla, spójrz na make_image_classifier narzędzia wiersza polecenia, które zostanie zainstalowane przez pakiet PIP tensorflow-hub[make_image_classifier] , lub w tym TFLite colab.
Ustawiać
import itertools
import os
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
print("TF version:", tf.__version__)
print("Hub version:", hub.__version__)
print("GPU is", "available" if tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU') else "NOT AVAILABLE")
TF version: 2.7.0 Hub version: 0.12.0 GPU is available
Wybierz moduł TF2 SavedModel, którego chcesz użyć
Na początek, należy https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_100_224/feature_vector/4 . Ten sam adres URL może być użyty w kodzie do identyfikacji SavedModel oraz w przeglądarce do pokazania jego dokumentacji. (Zauważ, że modele w formacie TF1 Hub nie będą tutaj działać.)
Można znaleźć więcej modeli TF2, które generują obraz funkcji wektorów tutaj .
Istnieje wiele możliwych modeli do wypróbowania. Wszystko, co musisz zrobić, to wybrać inny w komórce poniżej i kontynuować z notatnikiem.
model_name = "efficientnetv2-xl-21k" # @param ['efficientnetv2-s', 'efficientnetv2-m', 'efficientnetv2-l', 'efficientnetv2-s-21k', 'efficientnetv2-m-21k', 'efficientnetv2-l-21k', 'efficientnetv2-xl-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b0-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b1-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b2-21k', 'efficientnetv2-b3-21k', 'efficientnetv2-s-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-m-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-l-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-xl-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b0-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b1-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b2-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b3-21k-ft1k', 'efficientnetv2-b0', 'efficientnetv2-b1', 'efficientnetv2-b2', 'efficientnetv2-b3', 'efficientnet_b0', 'efficientnet_b1', 'efficientnet_b2', 'efficientnet_b3', 'efficientnet_b4', 'efficientnet_b5', 'efficientnet_b6', 'efficientnet_b7', 'bit_s-r50x1', 'inception_v3', 'inception_resnet_v2', 'resnet_v1_50', 'resnet_v1_101', 'resnet_v1_152', 'resnet_v2_50', 'resnet_v2_101', 'resnet_v2_152', 'nasnet_large', 'nasnet_mobile', 'pnasnet_large', 'mobilenet_v2_100_224', 'mobilenet_v2_130_224', 'mobilenet_v2_140_224', 'mobilenet_v3_small_100_224', 'mobilenet_v3_small_075_224', 'mobilenet_v3_large_100_224', 'mobilenet_v3_large_075_224']
model_handle_map = {
"efficientnetv2-s": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_s/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-m": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_m/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-l": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_l/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-s-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_s/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-m-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_m/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-l-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_l/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_xl/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b0/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b1/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b2/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_b3/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-s-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_s/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-m-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_m/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-l-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_l/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_xl/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b0/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b1/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b2/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k-ft1k": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_ft1k_b3/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b0": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b0/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b1": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b1/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b2": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b2/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnetv2-b3": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet1k_b3/feature_vector/2",
"efficientnet_b0": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b0/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b1": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b1/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b2": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b2/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b3": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b3/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b4": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b4/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b5": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b5/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b6": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b6/feature-vector/1",
"efficientnet_b7": "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/efficientnet/b7/feature-vector/1",
"bit_s-r50x1": "https://tfhub.dev/google/bit/s-r50x1/1",
"inception_v3": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/inception_v3/feature-vector/4",
"inception_resnet_v2": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/inception_resnet_v2/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v1_50": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v1_50/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v1_101": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v1_101/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v1_152": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v1_152/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v2_50": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v2_50/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v2_101": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v2_101/feature-vector/4",
"resnet_v2_152": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/resnet_v2_152/feature-vector/4",
"nasnet_large": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/nasnet_large/feature_vector/4",
"nasnet_mobile": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/nasnet_mobile/feature_vector/4",
"pnasnet_large": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/pnasnet_large/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v2_100_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_100_224/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v2_130_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_130_224/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v2_140_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v2_140_224/feature_vector/4",
"mobilenet_v3_small_100_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_small_100_224/feature_vector/5",
"mobilenet_v3_small_075_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_small_075_224/feature_vector/5",
"mobilenet_v3_large_100_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_large_100_224/feature_vector/5",
"mobilenet_v3_large_075_224": "https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_large_075_224/feature_vector/5",
}
model_image_size_map = {
"efficientnetv2-s": 384,
"efficientnetv2-m": 480,
"efficientnetv2-l": 480,
"efficientnetv2-b0": 224,
"efficientnetv2-b1": 240,
"efficientnetv2-b2": 260,
"efficientnetv2-b3": 300,
"efficientnetv2-s-21k": 384,
"efficientnetv2-m-21k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-l-21k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k": 512,
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k": 224,
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k": 240,
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k": 260,
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k": 300,
"efficientnetv2-s-21k-ft1k": 384,
"efficientnetv2-m-21k-ft1k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-l-21k-ft1k": 480,
"efficientnetv2-xl-21k-ft1k": 512,
"efficientnetv2-b0-21k-ft1k": 224,
"efficientnetv2-b1-21k-ft1k": 240,
"efficientnetv2-b2-21k-ft1k": 260,
"efficientnetv2-b3-21k-ft1k": 300,
"efficientnet_b0": 224,
"efficientnet_b1": 240,
"efficientnet_b2": 260,
"efficientnet_b3": 300,
"efficientnet_b4": 380,
"efficientnet_b5": 456,
"efficientnet_b6": 528,
"efficientnet_b7": 600,
"inception_v3": 299,
"inception_resnet_v2": 299,
"nasnet_large": 331,
"pnasnet_large": 331,
}
model_handle = model_handle_map.get(model_name)
pixels = model_image_size_map.get(model_name, 224)
print(f"Selected model: {model_name} : {model_handle}")
IMAGE_SIZE = (pixels, pixels)
print(f"Input size {IMAGE_SIZE}")
BATCH_SIZE = 16
Selected model: efficientnetv2-xl-21k : https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_xl/feature_vector/2 Input size (512, 512)
Skonfiguruj zbiór danych Kwiaty
Wejścia są odpowiednio przeskalowane dla wybranego modułu. Rozszerzanie zbioru danych (tj. przypadkowe zniekształcenia obrazu za każdym razem, gdy jest czytany) usprawnia szkolenie, zwł. podczas dostrajania.
data_dir = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'flower_photos',
'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz',
untar=True)
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz 228818944/228813984 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step 228827136/228813984 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step
def build_dataset(subset):
return tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=.20,
subset=subset,
label_mode="categorical",
# Seed needs to provided when using validation_split and shuffle = True.
# A fixed seed is used so that the validation set is stable across runs.
seed=123,
image_size=IMAGE_SIZE,
batch_size=1)
train_ds = build_dataset("training")
class_names = tuple(train_ds.class_names)
train_size = train_ds.cardinality().numpy()
train_ds = train_ds.unbatch().batch(BATCH_SIZE)
train_ds = train_ds.repeat()
normalization_layer = tf.keras.layers.Rescaling(1. / 255)
preprocessing_model = tf.keras.Sequential([normalization_layer])
do_data_augmentation = False
if do_data_augmentation:
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomRotation(40))
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomTranslation(0, 0.2))
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomTranslation(0.2, 0))
# Like the old tf.keras.preprocessing.image.ImageDataGenerator(),
# image sizes are fixed when reading, and then a random zoom is applied.
# If all training inputs are larger than image_size, one could also use
# RandomCrop with a batch size of 1 and rebatch later.
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomZoom(0.2, 0.2))
preprocessing_model.add(
tf.keras.layers.RandomFlip(mode="horizontal"))
train_ds = train_ds.map(lambda images, labels:
(preprocessing_model(images), labels))
val_ds = build_dataset("validation")
valid_size = val_ds.cardinality().numpy()
val_ds = val_ds.unbatch().batch(BATCH_SIZE)
val_ds = val_ds.map(lambda images, labels:
(normalization_layer(images), labels))
Found 3670 files belonging to 5 classes. Using 2936 files for training. Found 3670 files belonging to 5 classes. Using 734 files for validation.
Definiowanie modelu
Wystarczy umieścić klasyfikator liniowy na górze feature_extractor_layer z modułem Hub.
Dla prędkości, zaczynamy z nie nadającego się do szkolenia feature_extractor_layer , ale można również włączyć dostrajania dla większej dokładności.
do_fine_tuning = False
print("Building model with", model_handle)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
# Explicitly define the input shape so the model can be properly
# loaded by the TFLiteConverter
tf.keras.layers.InputLayer(input_shape=IMAGE_SIZE + (3,)),
hub.KerasLayer(model_handle, trainable=do_fine_tuning),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(class_names),
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(0.0001))
])
model.build((None,)+IMAGE_SIZE+(3,))
model.summary()
Building model with https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/efficientnet_v2_imagenet21k_xl/feature_vector/2
Model: "sequential_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
keras_layer (KerasLayer) (None, 1280) 207615832
dropout (Dropout) (None, 1280) 0
dense (Dense) (None, 5) 6405
=================================================================
Total params: 207,622,237
Trainable params: 6,405
Non-trainable params: 207,615,832
_________________________________________________________________
Trening modelki
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.005, momentum=0.9),
loss=tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True, label_smoothing=0.1),
metrics=['accuracy'])
steps_per_epoch = train_size // BATCH_SIZE
validation_steps = valid_size // BATCH_SIZE
hist = model.fit(
train_ds,
epochs=5, steps_per_epoch=steps_per_epoch,
validation_data=val_ds,
validation_steps=validation_steps).history
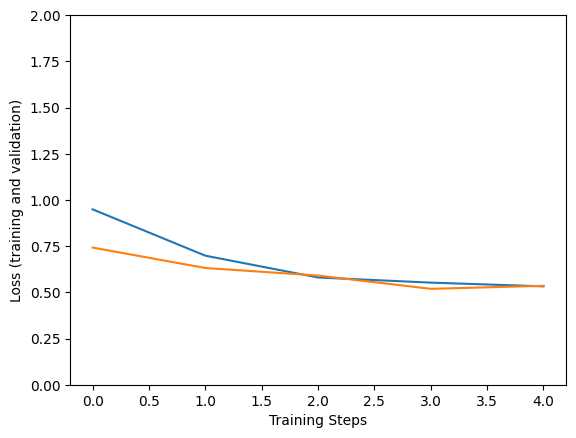
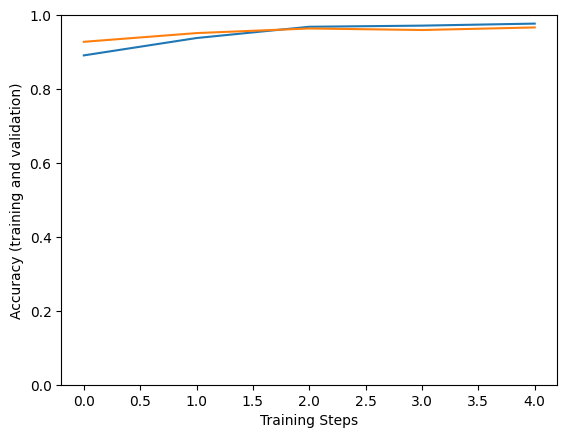
Epoch 1/5 183/183 [==============================] - 133s 543ms/step - loss: 0.9221 - accuracy: 0.8996 - val_loss: 0.6271 - val_accuracy: 0.9597 Epoch 2/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 514ms/step - loss: 0.6072 - accuracy: 0.9521 - val_loss: 0.5990 - val_accuracy: 0.9528 Epoch 3/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 513ms/step - loss: 0.5590 - accuracy: 0.9671 - val_loss: 0.5362 - val_accuracy: 0.9722 Epoch 4/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 514ms/step - loss: 0.5532 - accuracy: 0.9726 - val_loss: 0.5780 - val_accuracy: 0.9639 Epoch 5/5 183/183 [==============================] - 94s 513ms/step - loss: 0.5618 - accuracy: 0.9699 - val_loss: 0.5468 - val_accuracy: 0.9556
plt.figure()
plt.ylabel("Loss (training and validation)")
plt.xlabel("Training Steps")
plt.ylim([0,2])
plt.plot(hist["loss"])
plt.plot(hist["val_loss"])
plt.figure()
plt.ylabel("Accuracy (training and validation)")
plt.xlabel("Training Steps")
plt.ylim([0,1])
plt.plot(hist["accuracy"])
plt.plot(hist["val_accuracy"])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f607ad6ad90>]
Wypróbuj model na obrazie z danych walidacyjnych:
x, y = next(iter(val_ds))
image = x[0, :, :, :]
true_index = np.argmax(y[0])
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# Expand the validation image to (1, 224, 224, 3) before predicting the label
prediction_scores = model.predict(np.expand_dims(image, axis=0))
predicted_index = np.argmax(prediction_scores)
print("True label: " + class_names[true_index])
print("Predicted label: " + class_names[predicted_index])

True label: sunflowers Predicted label: sunflowers
Na koniec wyszkolony model można zapisać do wdrożenia w TF Serving lub TFLite (na urządzeniach mobilnych) w następujący sposób.
saved_model_path = f"/tmp/saved_flowers_model_{model_name}"
tf.saved_model.save(model, saved_model_path)
2021-11-05 13:09:44.225508: W tensorflow/python/util/util.cc:368] Sets are not currently considered sequences, but this may change in the future, so consider avoiding using them. WARNING:absl:Found untraced functions such as restored_function_body, restored_function_body, restored_function_body, restored_function_body, restored_function_body while saving (showing 5 of 3985). These functions will not be directly callable after loading. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/saved_flowers_model_efficientnetv2-xl-21k/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/saved_flowers_model_efficientnetv2-xl-21k/assets
Opcjonalnie: wdrożenie do TensorFlow Lite
TensorFlow Lite pozwala wdrożyć modele TensorFlow do urządzeń mobilnych i Internetu przedmiotów. Poniższy kod pokazuje jak konwertować wyszkolony model TFLite i zastosować narzędzia post-szkoleniowe z TensorFlow model optymalizacyjny Toolkit . Na koniec uruchamia go w interpreterze TFLite, aby sprawdzić wynikową jakość
- Konwersja bez optymalizacji daje takie same wyniki jak poprzednio (do błędu zaokrąglenia).
- Konwersja z optymalizacją bez żadnych danych kwantyzuje wagi modelu do 8 bitów, ale wnioskowanie nadal wykorzystuje obliczenia zmiennoprzecinkowe do aktywacji sieci neuronowych. Zmniejsza to rozmiar modelu prawie czterokrotnie i poprawia opóźnienia procesora na urządzeniach mobilnych.
- Co więcej, obliczenia aktywacji sieci neuronowych mogą być skwantowane do 8-bitowych liczb całkowitych, jeśli zapewniony jest mały zestaw danych referencyjnych do kalibracji zakresu kwantyzacji. Na urządzeniu mobilnym dodatkowo przyspiesza to wnioskowanie i umożliwia działanie na akceleratorach, takich jak Edge TPU.
Ustawienia optymalizacji
optimize_lite_model = False
num_calibration_examples = 60
representative_dataset = None
if optimize_lite_model and num_calibration_examples:
# Use a bounded number of training examples without labels for calibration.
# TFLiteConverter expects a list of input tensors, each with batch size 1.
representative_dataset = lambda: itertools.islice(
([image[None, ...]] for batch, _ in train_ds for image in batch),
num_calibration_examples)
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_path)
if optimize_lite_model:
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
if representative_dataset: # This is optional, see above.
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset
lite_model_content = converter.convert()
with open(f"/tmp/lite_flowers_model_{model_name}.tflite", "wb") as f:
f.write(lite_model_content)
print("Wrote %sTFLite model of %d bytes." %
("optimized " if optimize_lite_model else "", len(lite_model_content)))
2021-11-05 13:10:59.372672: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:363] Ignored output_format. 2021-11-05 13:10:59.372728: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:366] Ignored drop_control_dependency. 2021-11-05 13:10:59.372736: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:372] Ignored change_concat_input_ranges. WARNING:absl:Buffer deduplication procedure will be skipped when flatbuffer library is not properly loaded Wrote TFLite model of 826236388 bytes.
interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_content=lite_model_content)
# This little helper wraps the TFLite Interpreter as a numpy-to-numpy function.
def lite_model(images):
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
interpreter.set_tensor(interpreter.get_input_details()[0]['index'], images)
interpreter.invoke()
return interpreter.get_tensor(interpreter.get_output_details()[0]['index'])
num_eval_examples = 50
eval_dataset = ((image, label) # TFLite expects batch size 1.
for batch in train_ds
for (image, label) in zip(*batch))
count = 0
count_lite_tf_agree = 0
count_lite_correct = 0
for image, label in eval_dataset:
probs_lite = lite_model(image[None, ...])[0]
probs_tf = model(image[None, ...]).numpy()[0]
y_lite = np.argmax(probs_lite)
y_tf = np.argmax(probs_tf)
y_true = np.argmax(label)
count +=1
if y_lite == y_tf: count_lite_tf_agree += 1
if y_lite == y_true: count_lite_correct += 1
if count >= num_eval_examples: break
print("TFLite model agrees with original model on %d of %d examples (%g%%)." %
(count_lite_tf_agree, count, 100.0 * count_lite_tf_agree / count))
print("TFLite model is accurate on %d of %d examples (%g%%)." %
(count_lite_correct, count, 100.0 * count_lite_correct / count))
TFLite model agrees with original model on 50 of 50 examples (100%). TFLite model is accurate on 50 of 50 examples (100%).

